Deep Vein Thrombosis
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is when a thrombus (blood clot) occurs in the deep veins of your body, usually the legs. However, they can also develop in the chest, arms, and other areas of the body. Having symptoms of DVT can be serious to your health. Not only does it cause severe swelling and pain in the affected area, but the blood clots can get stuck in blood vessels, break loose, and travel to essential bodily functions, such as your lungs, brain, or even heart. Blood clots can cause severe organ damage and, in some cases, death.
What Causes Deep Vein Thrombosis?
A lack of blood flow causes Deep Vein Thrombosis. The main side effect of slow blood flow is blood clots. Causes of deep vein thrombosis’s poor blood flow vary. Some reasons may include:
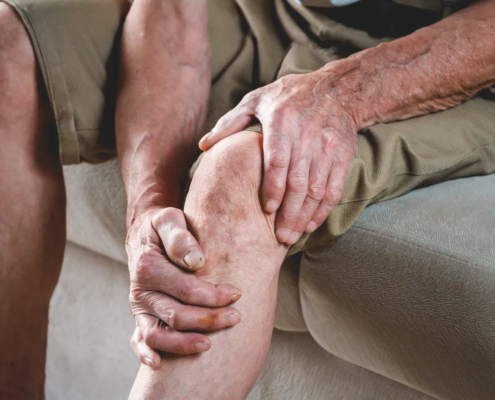
Immobility: Lack of mobility decreases blood flow. Being active throughout the day is recommended, even if it is only a 15-minute walk every few hours.
Accidents: Serious accidents can cause damage to the normal functionality of veins and cause blood flow to decrease in certain areas of the body.
Confinement: Confinement to a nursing home or hospital bed can cause decreased blood flow due to immobility. Calf muscles should be moved regularly to help veins push blood back up the body.
Surgery: More often than not, soon after any procedure that requires the reduction of blood flow to a part of the body, blood clots can form due to tissues, proteins, and fats loosening in the veins. Damage to vein walls can also release chemicals that trigger blood clots.
Weight: Being overweight or obese adds pressure to the veins circulating through the legs and pelvis.
Heritage: Some people may inherit blood clotting disorders that make them more prone to blood clotting.
Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis
A pulmonary embolism may be preventable with the treatment needed with deep vein thrombosis. A pulmonary embolism is caused when a large blood clot or several clusters of blood clots block a lung artery.
Severe conditions that may occur due to a deep vein thrombus breaking loose are lung damage, low oxygen, and damage to organs due to low oxygen levels. If there is a blood clot that is large enough or too many blood clots that get into an artery, death can occur.
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. 50% of people affected with a pulmonary embolism claim they did not have symptoms, so it is recommended to visit a doctor at least once or twice a year for a check-up.
Treatment for Deep Vein Thrombosis
There are a variety of treatment options for Deep Vein Thrombosis. In order to reduce the damage blood clots do to organs, anticoagulants must be used. There are several types of anticoagulation methods. Some of them are:
Consult with a doctor before the use of any of these methods.
Heparin: Blood thinner injection used to prevent blood clots.
LMWH: Low molecular weight heparin is used to prevent or treat a blood clot. Injections are given once or twice each day.
Vitamin K: Used for helping against blood clots and preventing excessive bleeding. Vitamin K is obtained from eating leafy greens, meats, cheeses, eggs, and synthesized bacteria.
Daily Recommended Vitamin K
- Age
- 0-6 months
- 7-12 months
- 1-3 years
- 4-8 years
- 9-13 years
- Girls: 14-18 years
- Pregnant or breastfeeding: >19 years
- Pregnant or breastfeeding: 19-50 years
- Boys: 14-18 years
- Men: 19+ years
- Micrograms per day
- 2 micrograms
- 2.5 micrograms
- 30 micrograms
- 55 micrograms
- 60 micrograms
- 75 micrograms
- 75 micrograms
- 90 micrograms
- 75 micrograms
- 120 micrograms
Post Thrombotic Syndrome
Around 50% of people who have experienced deep vein thrombosis can develop Post Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS). PTS symptoms include ulcers, sores, redness, rashes, chronic swelling, or leg pain. Inflammation in veins blocks blood flow and causes damage to the vein’s valves. When valves are damaged, they tend to leak, causing pools of fluids and blood, which can become blood clots.
Testimonials
Just wanted to thank you all for being such a great personable and professional staff. Working with each one of you has been so easy and I know you all were out for my best interest. Can’t thank you enough for caring the way you do. – CC
I just love you all and I’m very happy with everyone in the office there…everyone has been very nice and helpful and Dr Vincent is a great doctor! – Robin
Thank you all! I appreciate each and every one of you for my care. You all took the extra time to guide me and to teach each step of the way! You all made treatment easy and fun! What an awesome team! – Cheryl D
Vincent Vein Center was very willing to help when no one else would. Both legs are better – more than I ever thought or expected! I think you did very well by me. Thank you. – SH
